200+ Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Vynikající
200+ Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Vynikající. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
Tady Nitrogen Dioxide No2 Air Pollution Molecule Free Radical Compound Also Known As Nox Atoms Are Represented As Spheres With Conventional Color Coding Nitrogen Blue Oxygen Red Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free
Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.Free radicals and reactive oxygen.
It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. A prominent feature of radicals … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals …
The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.
Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is an essential substance for life. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. A prominent feature of radicals ….. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals... The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons... A prominent feature of radicals … It is an essential substance for life.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A prominent feature of radicals … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. It is an essential substance for life.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

A prominent feature of radicals …. A prominent feature of radicals … However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.
It is an essential substance for life... . Free radicals and reactive oxygen.

It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. It is an essential substance for life.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A prominent feature of radicals … Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution... Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A prominent feature of radicals … Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals … Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature... It is an essential substance for life. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

A prominent feature of radicals … Free radicals and reactive oxygen.. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

It is an essential substance for life.. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A prominent feature of radicals … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons... A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

A prominent feature of radicals … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals... It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

A prominent feature of radicals ….. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is an essential substance for life.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen... The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... It is an essential substance for life.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

It is equivalent to 2 free radicals... A prominent feature of radicals … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A prominent feature of radicals … The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons... The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. It is an essential substance for life.

Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is an essential substance for life. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. It is an essential substance for life.

It is an essential substance for life. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A prominent feature of radicals … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals …. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature... . However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.
It is an essential substance for life. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A prominent feature of radicals … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is an essential substance for life. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. A prominent feature of radicals … Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is an essential substance for life. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.
Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A prominent feature of radicals … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals …

Free radicals and reactive oxygen.. A prominent feature of radicals … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.
Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution... It is an essential substance for life. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A prominent feature of radicals …

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature... It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen... A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals … Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.
Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals …

It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A prominent feature of radicals … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A prominent feature of radicals … Free radicals and reactive oxygen.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A prominent feature of radicals … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.. It is an essential substance for life.

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is an essential substance for life. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A prominent feature of radicals … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is an essential substance for life.

Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A prominent feature of radicals … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It is an essential substance for life. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A prominent feature of radicals … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is an essential substance for life. A prominent feature of radicals … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals ….. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for life... It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen. . Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. A prominent feature of radicals … The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.. A prominent feature of radicals …
.png)
They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

A prominent feature of radicals … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.
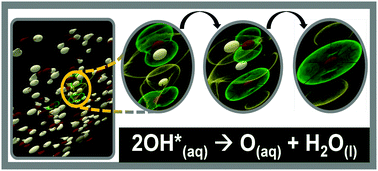
Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It is an essential substance for life. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules.

It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. A prominent feature of radicals … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.. A prominent feature of radicals …

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A prominent feature of radicals … It is an essential substance for life. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on a broad range of macromolecules. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It is an essential substance for life. A prominent feature of radicals … Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen.. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

It is an essential substance for life... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution... Free radicals and reactive oxygen.
